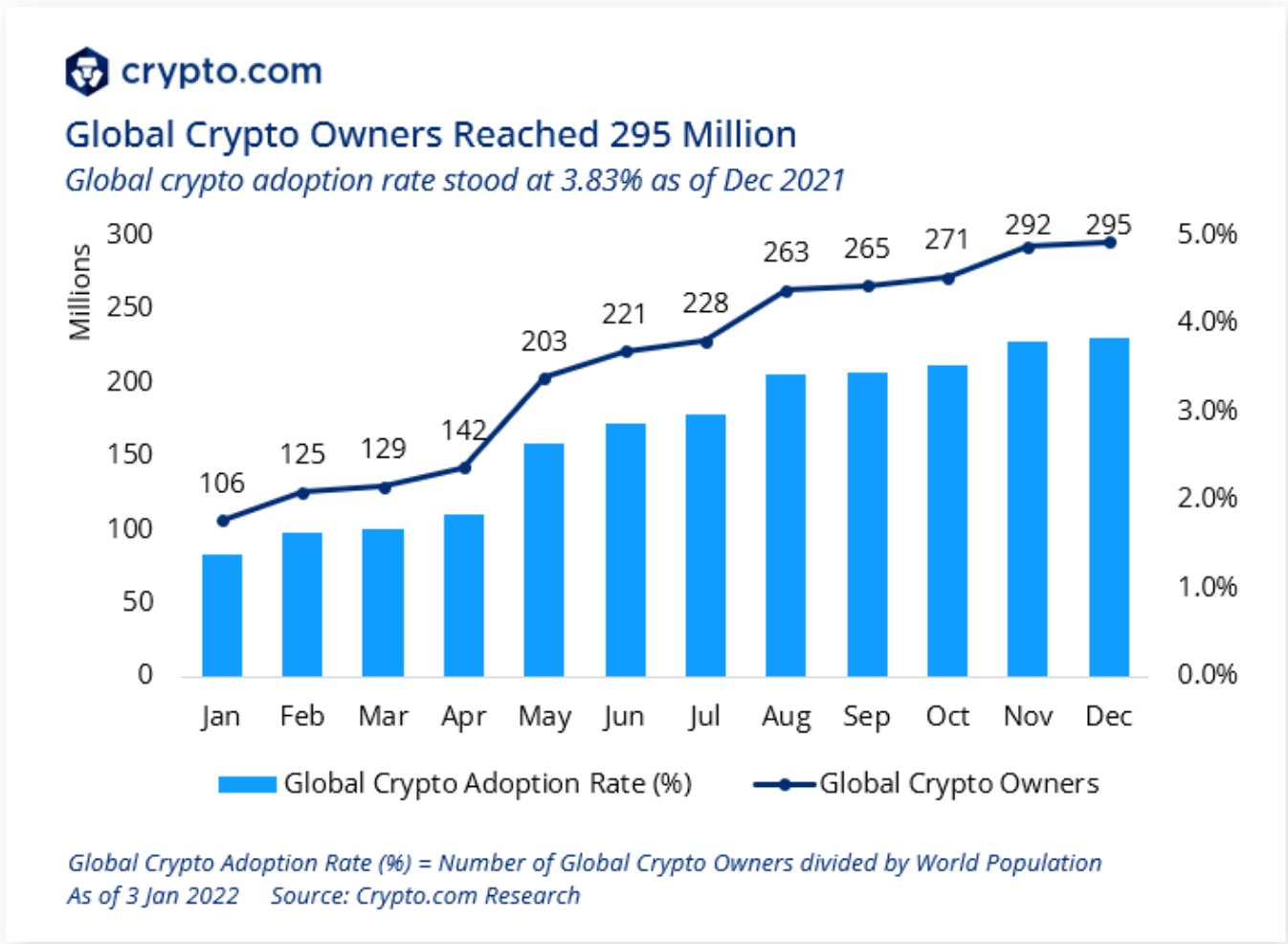
The cryptocurrency market has exploded in popularity and significance over the past decade, transforming from a niche interest among tech enthusiasts into a global phenomenon attracting investors, businesses, and governments alike. This decentralized digital asset class offers both immense opportunities and significant risks, making it crucial to understand its intricacies before diving in.
What is Cryptocurrency?
At its core, cryptocurrency is a digital or virtual currency that uses cryptography for security. Unlike traditional currencies issued by central banks, cryptocurrencies operate on a decentralized technology called blockchain. Blockchain is a distributed, immutable ledger that records all transactions across a network of computers. This decentralization makes cryptocurrencies resistant to censorship and control by any single entity.
Key Features of Cryptocurrencies:
- Decentralization: No central authority controls the network.
- Cryptography: Secure transactions and control the creation of new units.
- Transparency: All transactions are recorded on the public blockchain (pseudonymous, not anonymous).
- Immutability: Once a transaction is recorded, it cannot be altered or reversed.
- Limited Supply (in many cases): Some cryptocurrencies have a fixed supply, which can potentially increase their value over time.
The History of the Crypto Market:
The first cryptocurrency, Bitcoin, was created in 2009 by an anonymous entity known as Satoshi Nakamoto. Bitcoin was designed as a peer-to-peer electronic cash system, aiming to eliminate the need for intermediaries like banks.
The early years of Bitcoin were marked by slow adoption and skepticism. However, as more people learned about its potential, its value began to rise. The first major price surge occurred in 2013, attracting wider attention to the crypto market.
In the years that followed, numerous other cryptocurrencies, known as altcoins, emerged. These altcoins often aimed to improve upon Bitcoin's design or offer different functionalities. Ethereum, launched in 2015, introduced smart contracts, which are self-executing agreements written into code. This innovation paved the way for decentralized applications (dApps) and decentralized finance (DeFi).
Key Cryptocurrencies:
- Bitcoin (BTC): The original cryptocurrency, often referred to as "digital gold." It has the largest market capitalization and is widely accepted.
- Ethereum (ETH): The second-largest cryptocurrency, known for its smart contract capabilities and the foundation of many DeFi projects.
- Ripple (XRP): Designed for fast and low-cost international money transfers.
- Litecoin (LTC): An early altcoin that aims to be a faster and cheaper version of Bitcoin.
- Cardano (ADA): A blockchain platform focused on sustainability, scalability, and transparency.
- Solana (SOL): A high-performance blockchain that supports fast transaction speeds and low fees.
- Dogecoin (DOGE): A meme-based cryptocurrency that gained popularity through social media.
- Shiba Inu (SHIB): Another meme-based cryptocurrency that seeks to be an alternative to Dogecoin.
Factors Influencing the Crypto Market:
The crypto market is highly volatile and influenced by a variety of factors:
- Supply and Demand: Like any market, the price of cryptocurrencies is determined by the balance of supply and demand.
- Market Sentiment: News, social media trends, and overall investor confidence can significantly impact prices.
- Regulatory Developments: Government regulations and policies regarding cryptocurrencies can have a major effect on the market.
- Technological Advancements: New technologies and innovations in the blockchain space can drive interest and investment.
- Economic Conditions: Macroeconomic factors such as inflation, interest rates, and global economic growth can influence investor behavior.
- Security Breaches and Hacks: Security incidents involving cryptocurrency exchanges or wallets can negatively impact market sentiment.
- Adoption by Businesses: Increased acceptance of cryptocurrencies by businesses and merchants can boost their legitimacy and value.
- Media Coverage: Positive or negative media coverage can influence public perception and investment decisions.
Investing in Cryptocurrencies:
Investing in cryptocurrencies can be potentially rewarding but also carries significant risks. Here are some key considerations:
- Risk Tolerance: Cryptocurrencies are highly volatile, and prices can fluctuate dramatically. Investors should only invest what they can afford to lose.
- Due Diligence: Thoroughly research any cryptocurrency before investing. Understand its technology, use case, and team behind it.
- Diversification: Spread your investments across multiple cryptocurrencies to reduce risk.
- Security: Protect your cryptocurrency holdings by using secure wallets and enabling two-factor authentication.
- Long-Term Perspective: Consider investing for the long term rather than trying to time the market.
- Stay Informed: Keep up with the latest news and developments in the crypto market.
- Use Reputable Exchanges: Choose well-known and reputable cryptocurrency exchanges with strong security measures.
- Tax Implications: Be aware of the tax implications of buying, selling, or holding cryptocurrencies in your jurisdiction.
- Cold Storage: Consider using cold storage (offline wallets) for long-term holdings to minimize the risk of hacking.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi):
DeFi is a rapidly growing sector within the crypto market that aims to recreate traditional financial services in a decentralized manner. DeFi applications include:
- Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs): Platforms that allow users to trade cryptocurrencies directly with each other without intermediaries.
- Lending and Borrowing Platforms: Protocols that enable users to lend or borrow cryptocurrencies and earn interest.
- Yield Farming: Strategies that involve staking or lending cryptocurrencies to earn rewards in the form of additional tokens.
- Stablecoins: Cryptocurrencies pegged to a stable asset like the US dollar, designed to minimize price volatility.
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs):
NFTs are unique digital assets that represent ownership of items such as artwork, music, videos, or virtual real estate. NFTs have gained popularity as a way for creators to monetize their work and for collectors to own unique digital items.
The Future of the Crypto Market:
The future of the crypto market is uncertain, but several trends are likely to shape its development:
- Increased Regulation: Governments around the world are increasingly focusing on regulating cryptocurrencies, which could bring more stability and legitimacy to the market.
- Institutional Adoption: More institutional investors are entering the crypto market, bringing significant capital and expertise.
- Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs): Many central banks are exploring the possibility of issuing their own digital currencies, which could compete with or complement existing cryptocurrencies.
- Scalability Solutions: Ongoing efforts to improve the scalability of blockchain technology will be crucial for enabling wider adoption of cryptocurrencies.
- Sustainability: Concerns about the environmental impact of cryptocurrency mining are driving innovation in more energy-efficient consensus mechanisms.
- Integration with Traditional Finance: Cryptocurrencies are likely to become more integrated with traditional financial systems, blurring the lines between the two.
- Continued Innovation: New technologies and applications in the blockchain space will continue to emerge, driving further growth and innovation in the crypto market.
Risks and Challenges:
- Volatility: Extreme price swings can lead to significant losses.
- Security Risks: Exchanges and wallets are vulnerable to hacking and theft.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Lack of clear regulations can create uncertainty and hinder adoption.
- Complexity: Understanding the technology and economics of cryptocurrencies can be challenging.
- Scams and Fraud: The crypto market is prone to scams and fraudulent schemes.
- Environmental Impact: The energy consumption of some cryptocurrencies is a concern.
- Scalability Issues: Some blockchains struggle to handle high transaction volumes.
Conclusion:
The crypto market is a dynamic and rapidly evolving space with the potential to transform the financial landscape. While it offers exciting opportunities for investors and innovators, it also carries significant risks. By understanding the underlying technology, key factors influencing the market, and potential risks, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions about participating in this exciting new asset class. Whether cryptocurrencies become a mainstream form of payment or remain a niche investment, their impact on the world is undeniable, and their future development will be closely watched by investors, regulators, and the public alike.